Specifications
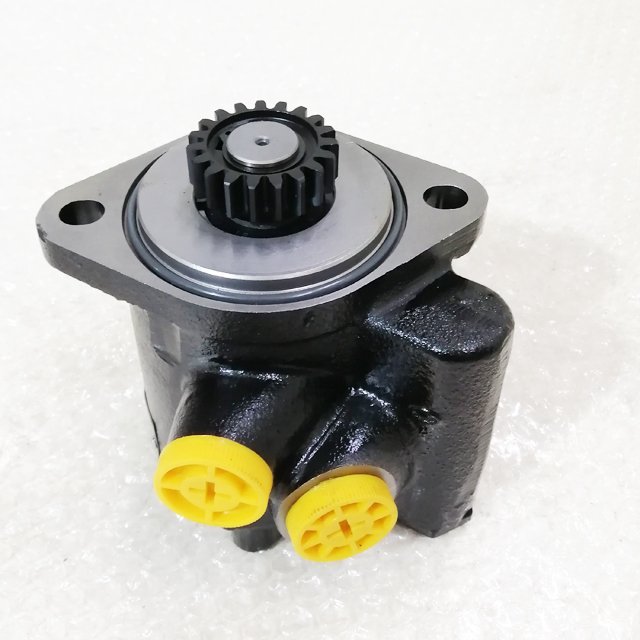
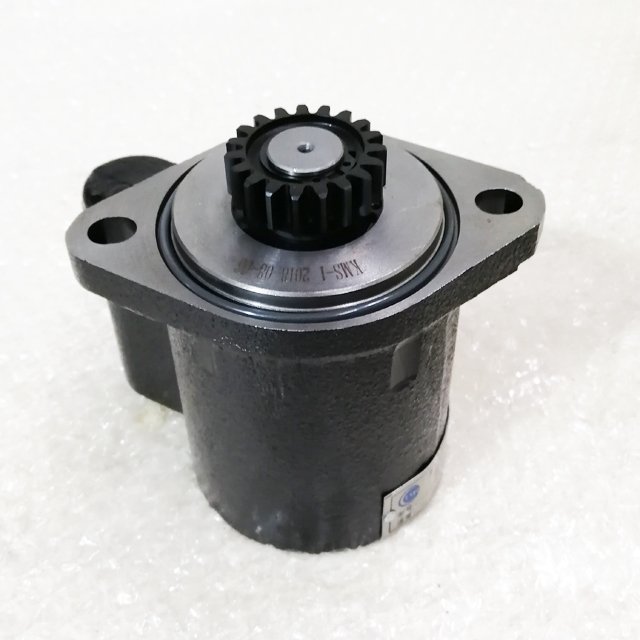
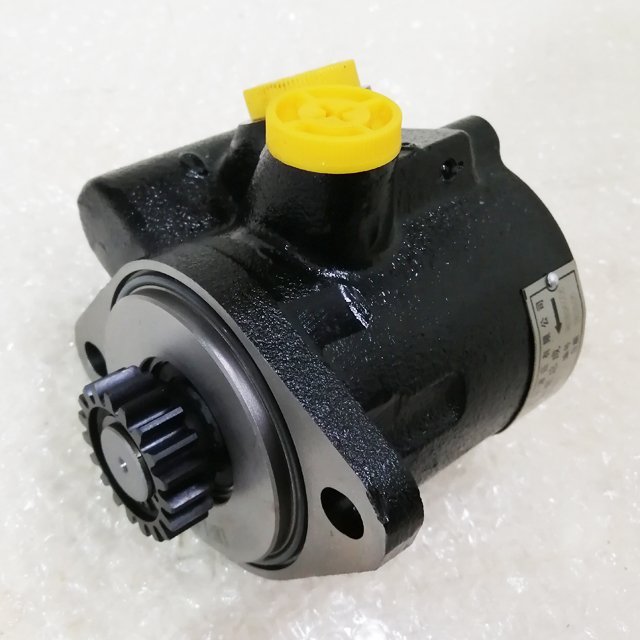
1.Part Name:Power Steering Pump
2.P/N: F31D1-3407100A
3.Suitable for Yuchai Parts.
4.MOQ: 1PC
5.100% new and good quality.
Advantages:
1.Competitive price.
2.High quality guaranteed: one year. (OEM & ODM)
3.Specializing in engine parts for more than 20 years.
4.OEM or brand package as your require.
5.Save your time, save your Money.
6.One stop solution for the engine parts.
Main Products
Supply XCMG Parts,Caterpillar Parts,Perkins Parts,Weichai Deutz Parts,Doosan Parts,John Deere Parts,Kobelco Parts,SDLG Parts,Yuchai Parts,Shantui Parts,some can be equipped with famous brands like Doosan, Sany, KOMATSU, HITACHI, KOBELCO, LIUGONG,XCMG, Deutz, etc.












-300x300.jpg)


